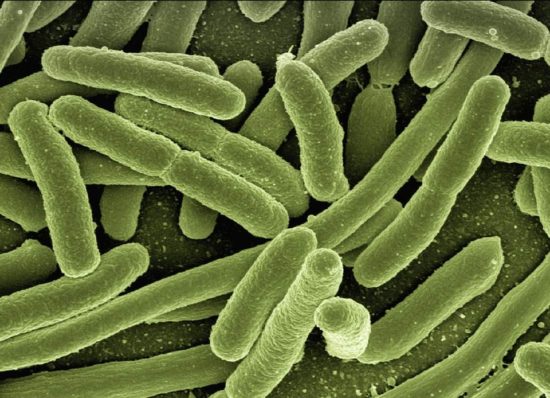
Modelling the implementation of narrow versus broader spectrum antibiotics in the empiric treatment of E. coli bacteraemia
This study evaluates the feasibility of switching to narrow spectrum antibiotics during empiric treatment of E. coli bacteraemia. It found that narrow spectrum antibiotics reduce resistance to second-line and third-line antibiotics but increase resistance to first-line therapy and higher mortality. Shortening treatment duration and reducing baseline mortality rate are crucial for increasing the feasibility of switching to narrow spectrum antibiotics. The study provides a flexible model design for other bacterial infections.
AMR NEWS
Your Biweekly Source for Global AMR Insights!
Stay informed with the essential newsletter that brings together all the latest One Health news on antimicrobial resistance. Delivered straight to your inbox every two weeks, AMR NEWS provides a curated selection of international insights, key publications, and the latest updates in the fight against AMR.
Don’t miss out on staying ahead in the global AMR movement—subscribe now!